Private sector engagement @ SDC
As recognized in international agreements such as the Sustainable Development Goals of the Addis Ababa Action Agenda for Financing for Development, the private sector has a key role to play in achieving the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development by contributing its resources, capacity for innovation and finance to address some of the world’s most pressing challenges.

The role of the private sector in sustainable development
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development as well as SDC’s overarching mandate to reduce poverty can only be achieved by joining forces with all relevant stakeholders in creative and effective partnerships. The innovative power, expertise and resources of the private sector must be harnessed for addressing global development challenges. Engaging with the private sector is a priority of Switzerland's International Cooperation strategy 2025-2028 and the SDC seeks to promote the cooperation with the private sector within all its thematic areas.
The private sector is an essential driving force for reducing global poverty and promoting sustainable solutions. In developing countries, nine out of ten jobs are provided by the private sector, and many companies bring innovative products and essential services to market that improve living conditions for poor and vulnerable groups. The international community and the private sector have recognized the need to work together to achieve the ambitious Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and to tackle today’s global challenges. Private sector engagement (PSE) as an approach in international development cooperation is one way to promote results-driven collaborations with positive impact.
Key criteria of private sector engagement at SDC
The Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) has a long history of collaboration with different private sector actors in the context of specific development projects or in multi-stakeholder platforms. These interactions with private sector actors can take multiple shapes and forms, in which the SDC and the private sector hold different roles.
PSE is one specific form of collaboration with the private sector. It refers to partnerships in which the SDC and one or several private sector actors join forces (either directly or indirectly) on an equal footing for an impact-driven development intervention, based on shared values, benefits, risks and costs.
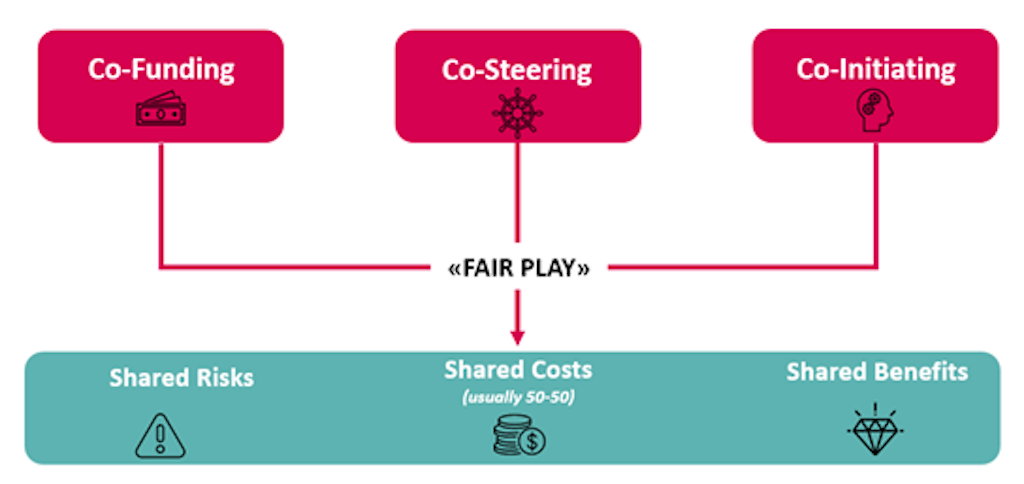
The three core attributes of private sector engagement are “co-funding”, “co-steering” and “co-initiation” of the intervention. The combination of these core attributes paired with an appropriate structuring of the partnership is meant to ensure fair and balanced collaboration (“fair play”) among partners, with shared costs, risks, and benefits (see Figure 1).
- Co-funding refers to the joint contribution of resources for the PSE partnership, which is a fundamental requirement (PSE does not exist without co-funding from the private sector). The contribution provided by the private sector partner can be cash or in-kind (including staff time, products, or services).
- Co-steering refers to a formalized governance mechanism through which the SDC and the private sector partner(s) jointly guide, oversee, and influence the direction and implementation of the partnership. Typically, both the SDC and the private sector partner(s) actively participate in the governing body of a PSE collaboration. Co-steering is a fundamental requirement for a PSE and can take many forms.
- Co-initiation refers to the joint establishment of a collaboration, including the identification of new ways to address development challenges. The spirit of co-initiation, co-creation, or co-design is meant to foster shared responsibility and accountability. Co-initiation is not always applicable in practice; in some cases, the SDC may join an already established partnership or take part in an existing structure. Therefore, co-initiation is an optional element in PSE collaborations.
Co-ownership and co-funding of the intervention is what differentiates PSE from other forms of interaction with the private sector, for example, private sector development.
On top of those core attributes, PSE collaborations must adhere to strict principles, such as compatibility with the SDC’s objectives, additionality, subsidiarity, non-distortion of markets, due process and compliance with social, environmental & governance criteria.
PSE arrangements may be “direct” or “indirect”:
- Direct PSE projects refer to arrangements in which the SDC engages directly with one or several private sector actors and signs legal agreements with them defining the rules of the partnership (e.g., a contract, memorandum of understanding or equivalent). There is no intermediary structure or partner between the SDC and the private sector partner(s).
- Indirect PSE projects refer to arrangements in which the SDC does not engage directly with private sector actor(s), and in which its partnership with private sector actor(s) is managed by an intermediary organization. In this scenario, the SDC has a contractual arrangement with the intermediary organization, which manages all legal arrangements with the private sector partners
The distinction between direct and indirect PSE projects is important for the analysis and structuring of PSE arrangements, especially with regard to PSE risk assessment.
PSE partnerships can be initiated with a variety of of well-established private sector actors with diverse profit-driven approaches and risk appetites. In the PSE context, the private sector encompasses 100% private owned companies as well as non-majority-state-owned organizations, including both profit-oriented companies and less profit-maximizing or non-profit entities such as social enterprises, impact-driven businesses, and philanthropic foundations. Private sector actors can be national or international.
Engaging with the private sector is a modality of intervention – a means to an end – complementing other forms of development cooperation. PSE is not a standalone solution, nor is it appropriate in every context. But when well designed, it adds value and complements other development instruments. SDC aims to expand and strengthen private-sector partnerships across all themes and regions.
Scaling up PSE is about engaging more strategically and tailoring approaches to each context. To mobilize greater investment in underserved markets, SDC sees strong potential in catalytic concessional finance to de-risk private investment. This shift from a purely grant-based to an investment-oriented approach enables SDC to mobilize additional resources, especially in areas where it has strong expertise such as food security, sustainable agriculture, renewable energy, climate resilience, financial inclusion, water, health, and education.
Key documents
The General Guidance on the Private Sector in the Context of the International Cooperation Strategy and the revised SDC Handbook on Private Sector Engagement are the main guiding documents for PSE collaborations at SDC. Please find the documents below.
While the revised PSE Handbook describes the main purpose and principles of private sector engagement, additional operational details are provided in a set of Technical Guidance Notes designed for SDC staff as internal documents, and which cover key PSE implementation topics. These documents can be accessed via the FDFA intranet here